A Guide to Quality Assurance Process Improvement
Discover proven quality assurance process improvement strategies. Learn to optimize workflows, integrate automation, and build a culture of continuous quality.

When we talk about improving a quality assurance process, we're really talking about a fundamental shift in mindset. It's about moving from a reactive "bug hunt" to a proactive culture of building quality in from the start. This means refining everything from your daily workflows and toolchains to how your teams collaborate. Get this right, and you'll do more than just ship better products—you'll release faster, lower costs, and keep your customers happy.
Auditing Your Current QA Reality

Before you can fix anything, you have to get a brutally honest look at where you are right now. A proper audit isn't about flipping through dusty process documents; it's about digging into the messy, day-to-day reality of how your team actually works. The goal here is to draw a clear map of your current state, warts and all, so you can see precisely what’s working and what's holding you back.
This means gathering both hard numbers and human stories. Sure, you need bug counts, but you also need to understand the why behind those numbers. For example, a spike in reopened tickets might not mean the bugs are complex—it could be a sign of a communication breakdown between your QA and dev teams.
Identifying Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Your first mission is to find the friction. Where are things slowing down? Where are people getting frustrated? Look for those recurring headaches that signal a deeper systemic issue. A good audit always shines a light on these common hiding spots for inefficiency.
- Manual Regression Cycles: Be honest—are your manual regression suites constantly pushing release dates? Track the hours burned on these tests and how often they cause delays.
- Environment Mismatches: How many times have you heard, "But it worked in staging!"? If bugs keep showing up in production that were impossible to find in your test environments, you have a critical disconnect that needs fixing.
- Insufficient Test Data: Do strange edge-case bugs keep slipping into the wild? This is a classic symptom of using test data that doesn't mirror what your actual users are doing.
- Vague Bug Reports: Look at the comment history on your bug tickets. If developers are constantly pinging testers back for more information—screenshots, logs, replication steps—your bug reporting process itself is a major bottleneck.
Mapping Communication and Workflows
Once you’ve identified these pain points, it’s time to visualize the process. Grab a whiteboard or a flowchart tool and physically map out how a feature travels from an idea to a deployed reality. This simple act is incredibly revealing, often exposing redundant steps, communication black holes, and confusing handoffs you never knew existed.
When you're done, you should have a solid, documented baseline. This isn't just a list of grievances; it's a prioritized inventory of genuine opportunities for quality assurance process improvement. This clarity is the bedrock of any successful change, ensuring you're focusing your energy on solving problems that truly matter.
Shifting Quality Left and Right
Let's be honest: truly effective quality assurance isn't just a final checkpoint before launch. If you're still treating QA as the last gate your product has to pass through, you're missing the point. It needs to be a mindset, woven into the entire development lifecycle.
To get there, we need to stop just finding bugs and start preventing them. This isn't just a small tweak; it's a fundamental change in approach that revolves around two powerful ideas: shifting left and shifting right.
Weaving Quality into the Early Stages
The Shift-Left principle is simple in concept but profound in practice. It’s all about pulling testing and quality-focused activities much, much earlier in the process. I'm talking way before a feature is even considered "code complete." Quality checks should be happening during the requirements and design phases.
Think about it. It’s far cheaper and faster to fix a flaw on a whiteboard than it is to fix it in production.
This completely changes the team dynamic. Developers are no longer just lobbing code over a wall to testers. Instead, QA experts and developers become partners from day one. This collaboration is where the magic happens, catching everything from logical flaws to clunky usability issues long before anyone commits a single line of code.
I’ve seen this play out countless times. A QA engineer sits in on a design review, looks at a mockup, and immediately spots a user workflow that’s confusing or incomplete. The developers would have built it exactly as specified, but that early flag saves the team dozens—sometimes hundreds—of hours of coding, testing, and inevitable rework.
It boils down to asking the tough questions right at the start:
- Are these requirements actually testable? Are they crystal clear?
- Does this design handle edge cases and what happens when things go wrong?
- Did anyone think about the performance hit this new feature might cause?
Gaining Insights from the Real World
While shifting left is all about prevention, Shift-Right is its perfect complement. This is where we get real-world feedback by testing and monitoring the software after it’s been deployed. It’s a humble acknowledgment that no matter how much testing you do in a staging environment, you can never fully replicate the beautiful chaos of production.
This is where practices like A/B testing, canary releases, and feature flagging come into play. These aren't just deployment strategies; they are powerful forms of post-release testing. They let you roll out changes with a safety net, gathering direct feedback on performance, stability, and what your users actually think.
This evolution is fundamentally changing how we measure success in QA. Old-school metrics like raw bug counts are becoming less important. Instead, modern teams are focused on indicators like ‘time to feedback’ and, most critically, a steady reduction in production-level bugs. You can learn more about how preview environments and team-wide engagement are revolutionizing this process.
When you combine both left and right shifts, you create a powerful, continuous feedback loop. Early collaboration prevents the most common defects, while post-release monitoring gives you the hard data needed to refine the product and improve your quality assurance process improvement strategy for the next cycle. It’s a complete, 360-degree approach to quality.
Automating Smarter, Not Harder, with AI

In today's fast-paced development world, trying to keep up with quality using only manual testing is a losing battle. It’s not just about moving faster; it's about being smarter and more resilient. This is where a strategic approach to automation and artificial intelligence can completely change the game for your QA team.
We're not just talking about running the same old scripts faster. Think about AI-driven tools that can intelligently generate their own test cases, navigate extremely complex user flows, and even heal themselves when a button or menu on the screen moves. For anyone who has spent hours fixing tests after a minor UI tweak, that self-healing capability is a massive relief.
Predicting Problems Before They Happen
One of the most impressive things I've seen AI do for QA is predict where bugs are most likely to show up. By sifting through years of bug reports, code commits, and complexity metrics, AI algorithms can pinpoint the riskiest parts of your application. This lets you aim your team's valuable time and effort exactly where it matters most.
Imagine this: your CI/CD pipeline flags a new feature. Not because it failed a specific test, but because its code pattern is eerily similar to a module that has historically caused 35% of all your critical bugs. That’s the kind of proactive insight that shifts your quality assurance process improvement from a reactive fire drill to a data-informed strategy.
Choosing the Right AI Tools and Frameworks
The market is flooded with AI-powered QA tools, so choosing the right one is crucial. Don't get distracted by the latest buzz. Instead, find a tool that solves a genuine problem you're facing right now and fits into your existing workflow.
When you're evaluating options, here are a few things I always look for:
- Smooth Integration: How well does it connect with your current CI/CD pipeline, bug tracker, and project management software? A tool that doesn't play well with others just creates more work.
- Self-Healing Capabilities: Ask for a demo of how the tool handles changes to your application's UI. Strong visual recognition is key to reducing the time you spend on test maintenance.
- Actionable Reporting: Does the tool give you clear insights or just a mountain of pass/fail data? You want analytics that help you spot trends and make better decisions over time.
Building a solid automation framework is ultimately about more than just the tools you buy. It demands a shift in mindset, where developers and QA engineers work together to build and maintain the test suite. With that kind of shared ownership, your automated tests become a lasting asset. And when you combine smart automation with other intelligent systems, you can even explore how AI can assist product management by feeding them real-time quality data.
Upgrading Your QA Toolchain
The right tools can make or break your entire quality process. I've seen teams get bogged down by clunky, disconnected software that just adds friction, while others fly with a toolchain that amplifies every effort. A modern QA setup isn't just a list of licenses; it’s a fully integrated ecosystem.
Think of it as the central nervous system for your quality efforts. When data flows seamlessly between your test management system, CI/CD pipeline, and bug tracker, you get a single source of truth. This is a non-negotiable part of any real quality assurance process improvement plan. The goal is to get all these systems speaking the same language so your team can spot and squash problems faster.
What Modern QA Tools Look Like
The market for continuous improvement tools is absolutely exploding—it's expected to hit USD 38.15 billion in 2024. A big driver behind this is the adoption of technologies like Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), which are completely changing the game for things like complex hardware inspections and user testing.
In fact, over 3,500 large companies are already using AR and VR to create risk-free training environments and simulate real-world operational scenarios. It's a fascinating shift, and you can explore more about these quality management trends to see where the industry is heading.
While AR is exciting, every team needs a solid foundation. You've got to have the essentials covered:
- Performance and Load Testing: To make sure your app doesn't crumble under real-world traffic.
- Security Scanning: To find and fix vulnerabilities before they turn into a full-blown crisis.
- API Validation: To ensure the critical data pipelines between your services are solid and reliable.
The proof is in the numbers. Just look at the difference a strategic toolchain upgrade can make when you compare the before and after.
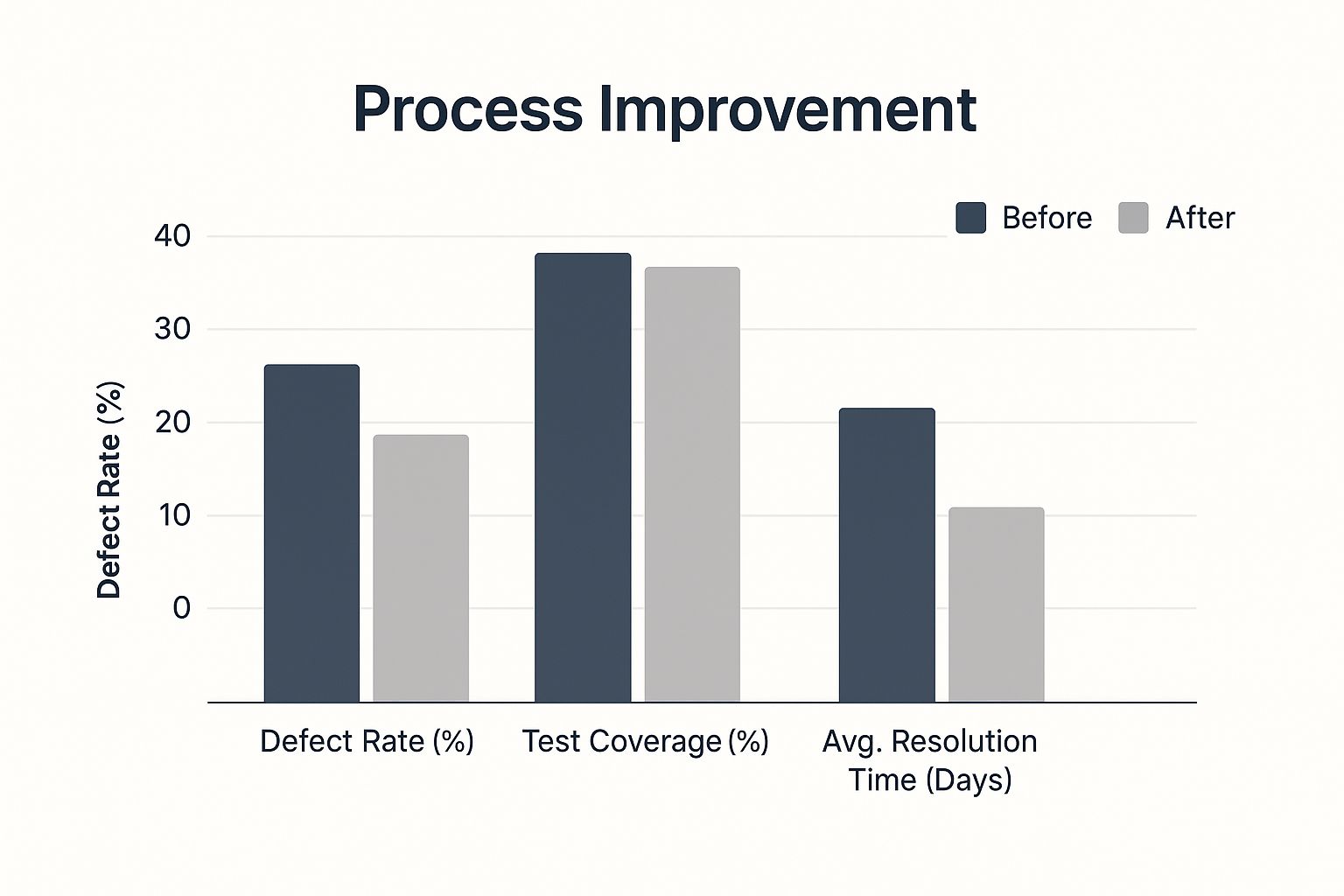
As you can see, a thoughtful investment here leads to a dramatic drop in defect rates and resolution times, all while significantly boosting test coverage.
A modern QA process is supported by a variety of specialized tools. Here's a breakdown of the key categories and the role they play.
Modern QA Tool Categories and Use Cases
| Tool Category | Primary Function | Impact on QA Process |
|---|---|---|
| Test Management Platforms | Centralize test cases, plans, and results. | Provides a single source of truth for all testing activities and tracks progress against quality goals. |
| Automation Frameworks | Execute repetitive tests programmatically. | Frees up QA engineers to focus on complex exploratory testing and increases test coverage. |
| CI/CD Pipeline Tools | Automate the build, test, and deployment cycle. | Enables continuous testing and ensures quality checks are an integral part of every code change. |
| Bug & Issue Trackers | Capture, prioritize, and manage defects. | Streamlines the defect lifecycle from discovery to resolution, providing clear accountability. |
| Performance Testing Tools | Simulate user load to measure system stability. | Identifies bottlenecks and ensures the application can handle peak traffic without crashing. |
| Security Scanning Tools | Identify vulnerabilities in code and infrastructure. | Proactively hardens the application against attacks, reducing security risks before release. |
Ultimately, choosing tools from these categories helps build a comprehensive system that addresses quality from every angle.
Creating a Connected and Integrated System
The real magic happens with integration. When your bug tracker automatically pulls in logs from your monitoring tool, or your test management platform triggers a new build after a test run, you're eliminating manual work and slashing the risk of human error.
This kind of connectivity is what creates tight, effective feedback loops. Developers get faster, richer context on bugs, and product managers can see the real-time quality status of new features. A well-integrated toolset is crucial for smart decision-making, which is why we put together a guide on the best tools for product managers.
At the end of the day, a smart collection of integrated tools doesn't just support your QA process—it actively accelerates it.
Measuring What Matters for Lasting Improvement

You can't fix what you can't see. When it comes to improving your quality assurance process, everything hinges on tracking the right data. It's easy to get sidetracked by vanity metrics, like the sheer number of test cases you run. While a big number might look good on a report, it often creates a false sense of security and tells you very little about the actual health of your product.
Real improvement comes from measuring what genuinely impacts your users and your business. We need to shift our focus to key performance indicators (KPIs) that tell a clear story about product stability, team efficiency, and ultimately, customer happiness.
Moving Beyond Vanity Metrics
The first thing we have to do is redefine what success looks like. Instead of patting ourselves on the back for a high volume of passed tests, let's start tracking metrics that have tangible consequences. A well-designed dashboard built around these KPIs gives everyone, from engineers to executives, a clear, actionable view of quality.
Here are a few essential metrics I always recommend starting with:
- Defect Escape Rate: This is the big one. It’s the ultimate report card for your QA process. This metric tracks the percentage of bugs that slip through all your checks and make it into production, where your customers find them. A consistently low escape rate is the hallmark of a truly effective quality process.
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): Once a bug is found, how long does it take your team to squash it? MTTR measures the efficiency of your entire defect lifecycle, from the initial report all the way to the deployed fix. A shorter MTTR is a great sign of an agile and responsive team.
- Test Automation Coverage: This isn't just about chasing a high percentage. Meaningful coverage is about being strategic. You should focus your automation efforts on critical user journeys and high-risk features. Aim for deep coverage on the parts of your application that matter most, not just an arbitrary overall number.
Fostering a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Data is only valuable when it sparks change. The most critical part of this whole process is what you do with the information you gather. This is your chance to build tight feedback loops that ensure your quality process is always getting better.
One of the best ways to put this into practice is by holding regular, blameless retrospectives. Let your dashboard guide the conversation. If MTTR spiked last month, the question isn't "Who dropped the ball?" but rather "What in our process created the delay?" Maybe it was a communication breakdown or a clunky deployment pipeline.
This data-driven approach takes the blame out of the equation and gets the team focused on fixing systemic issues. By tying your QA metrics directly to business outcomes, you create a powerful case for investing in quality. Digging into different customer satisfaction measurement methods can also add another layer of insight, connecting your internal quality efforts to how users actually feel about your product.
Ultimately, this cycle of measuring, analyzing, and adapting is what elevates QA from a simple gatekeeper to a strategic part of the business.
Frequently Asked Questions
When you're knee-deep in a quality assurance improvement project, questions are bound to pop up. Here are some straightforward answers to the things teams often ask as they work on their QA strategies.
What's the Real Difference Between QA and QC?
It's a common point of confusion, but Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) are two sides of the same coin. The easiest way to think about it is this: QC is reactive, while QA is proactive.
- Quality Control (QC): This is all about finding defects in the final product before it gets into a customer's hands. Think of it as the classic inspection phase—catching mistakes that have already been made.
- Quality Assurance (QA): This is a much bigger picture. QA is about designing the entire development process to prevent defects from ever happening. It's about building quality in from the very beginning.
So, while QC focuses on defect detection, QA is all about defect prevention.
How Can We Actually Measure if Our QA Improvements Are Working?
You need to know if your hard work is paying off. To do that, you have to move beyond just counting bugs and look at metrics that show a real impact on the business.
Here are a few key performance indicators I always recommend tracking:
- Defect Escape Rate: This is the big one. It's the percentage of bugs that slip through the cracks and are found by actual customers. If this number is going down, your process is getting stronger.
- Mean Time to Resolution (MTTR): How long does it take your team to fix a bug once it's been reported? A lower MTTR usually points to a much healthier, more collaborative workflow between developers and QA.
- Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT/NPS): At the end of the day, it's about the user. A rise in customer satisfaction scores is often a direct result of a higher-quality product experience.
We Want to Improve Our QA Process. Where Do We Even Start?
The most important first step is to run a full audit of your current process. You can't fix what you don't fully understand.
This means sitting down and mapping out your existing workflows, pinpointing where the recurring bottlenecks are, and getting honest, unfiltered feedback from everyone on the team.
Once you have that baseline, you can set clear, measurable goals. For instance, if your audit shows that manual regression testing is a major drag on every release, a great first objective would be to automate 20% of your most critical regression tests in the next three months.
Starting with a proper diagnosis is everything—it ensures you're putting your energy where it will make the biggest impact.
At SigOS, we take the guesswork out of this process. We use AI to analyze your customer data and pinpoint the exact issues that are hurting your bottom line. Our platform sifts through support tickets, sales calls, and usage data to show you which bugs are costing you real money and which features will actually drive growth.
Discover how SigOS can quantify the dollar value of your bugs and help you build a better product.
Keep Reading
More insights from our blog
Ready to find your hidden revenue leaks?
Start analyzing your customer feedback and discover insights that drive revenue.
Start Free Trial →

